EDI 856
Advance Ship Notice
EDI 856 Explained
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) 856, also known as the Advance Shipping Notice (ASN), is a crucial part of the supply chain. It lets suppliers inform customers about upcoming deliveries. The notice includes important details like order info, product descriptions, and carrier details, making the receiving process smoother.
By using EDI 856, businesses can improve their distribution and warehouse operations through better scheduling and fewer errors in handling shipments. Many industries, such as retail, manufacturing, and distribution, now require the EDI 856 because it ensures a consistent way of exchanging shipping data. This helps businesses plan their inventory and workforce more efficiently, leading to better decision-making. Overall, it showcases how technology enhances supply chain management from dispatch to delivery.
If diving deep into the details of EDI 856 isn’t your thing, Better EDI simplifies the process for you.
Our solution enables you to generate compliant Ship Notices effortlessly while also producing GS-1 labels that meet retailer standards.
Pricing right on our website, Get Started today!
Key Components of an ASN
- Shipment Details: Carrier information, tracking numbers, and transportation mode.
- Order Information: Purchase order numbers directly correlating with the EDI 850 transaction.
- Product Descriptions: Descriptions and identifiers, such as UPC or SKU.
- Packaging Types: Information on how the items are packed and labeled.
- Corresponding Labels: GS-1 Lables that match the pack/pallet information in a ship notice
The Structure of an EDI 856 Document
This document contains detailed information about the shipped items and their physical characteristics, meticulously organized in a sequence of segments and elements.
Beginning Segment: ISA and GS
The ISA (Interchange Control Header) and GS (Functional Group Header) segments mark the beginning of the EDI 856 document. The ISA is the start of the electronic envelope enclosing all the transactions, signifying who the sender and receiver are with precise identifiers. The GS follows to indicate the start of a functional group and provide control information.
Ship Notice/Manifest Header: BSN
The BSN (Beginning Segment for Ship Notice) acts as the header for the EDI 856 transaction set, assigning a unique identifier and date to the shipment notice. It indicates the beginning of the ship notice/manifest group and is critical for tracking and reference.
Hierarchical Structure: HL
The HL (Hierarchical Level) segment is used to structure the document in a multi-level, hierarchical format. Each HL segment within the 856 identifies a different level of detail, such as shipment, order, item, or pack, enabling a nested, parent-child relationship between the items shipped.
Detail Segment: LIN
The LIN (Item Identification) segment is where specific details of the items being shipped are provided. It includes information such as item identifiers, descriptions, and quantities. This segment might also contain additional item-related segments like MAN (Marks and Numbers), SN1 (Item Detail (Shipment)), or REF (Reference Identification).
Summary Segment: CTT and SE
At the end of the EDI 856, the CTT (Transaction Totals) segment summarizes the contents of the transaction set, providing counts like the number of line items shipped. The SE (Transaction Set Trailer) segment concludes the transaction set by specifying the total number of included segments and the sequence of the transaction within the functional group.
This structure, with its specific segments like ST (Transaction Set Header) and GE (Functional Group Trailer), as well as transportation-related segments such as TD1, TD5, and N1, ensures a standardized, comprehensive, and precise electronic communication of shipment details.
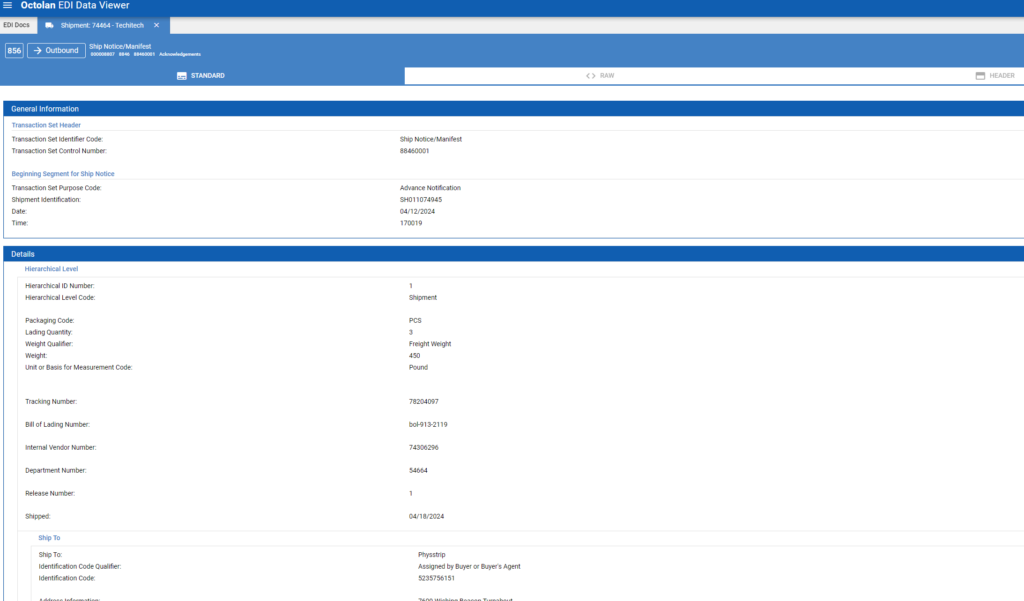
EDI 856 Implementation
When implementing the EDI 856 transaction, businesses must consider the technical aspects of communication protocols and the use of Value Added Networks (VAN), the specific needs and capabilities of suppliers, and the integration process with existing ERP systems. This ensures a seamless flow of shipment information between trading partners.
Communication Protocols and VAN
Implementing EDI 856 involves establishing a secure and reliable communication protocol. Common protocols include FTP, SFTP, AS2, and HTTP/S. Companies may choose to use a Value Added Network (VAN) as an intermediary to facilitate EDI exchanges. The VAN provides additional services such as mailboxing, translation, and compliance checking, thus often simplifying the setup process for businesses.
Considerations for Suppliers
For suppliers, delivering EDI 856, also known as the Advance Ship Notice or ASN, requires alignment with customer requirements. This includes adhering to specific data elements such as supplier code and shipment dates. Suppliers must evaluate their resources and may need to automate processes to ensure timely and accurate EDI transmissions. Effective collaboration between trading partners is crucial to address any potential issues in data quality or transmission.
Integrating EDI 856 With ERP Systems
Integrating EDI 856 with a company’s ERP system can streamline operations and reduce manual data entry. The right EDI solution should be compatible with the ERP software, enabling automated data flow between the systems. This integration allows for real-time access to shipment statuses and improved inventory management. Companies should allocate sufficient resources to ensure a smooth implementation and consider whether they require a direct integration or the use of middleware.
By considering these factors and employing the appropriate EDI solutions, businesses can successfully implement EDI 856 to enhance their supply chain efficiency and collaboration with trading partners.
Business and Technical Benefits
EDI 856, commonly known as the Advance Ship Notice (ASN), provides comprehensive benefits from both a business and technical standpoint. This electronic document facilitates enhancements in supply chain operations and data management, particularly benefiting retailers and distributors.
Streamlined Supply Chain Operations
The implementation of EDI 856 greatly streamlines supply chain operations. By providing detailed information about the contents and shipping of orders, it allows all parties involved to prepare for receipt and inventory management before the goods arrive. This level of anticipation enhances the efficiency of loading docks and distribution centers, ensuring that retailers and distributors can process shipments quickly.
Error Reduction and Data Accuracy
Since information transfer is automated, the probability of human error during data entry is minimized. Moreover, the accuracy of the data is improved as the ASN includes critical information, such as the tracking number, that helps verify the contents against the purchase order.
Advantages for Retailers and Distributors
For retailers and distributors, the EDI 856 is a powerful tool that enhances visibility into the supply chain. It assists in planning and inventory management, allowing for better forecasting and stock allocation. By utilizing this system, businesses can optimize shelf restocking and reduce overstock or stockouts. The precise and real-time data provided by ASN contribute to a more efficient and responsive supply chain.
Operational Challenges and Solutions
When managing Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) 856, which is the Advance Ship Notice (ASN), businesses encounter specific operational hurdles. Effective solutions to these issues are pivotal for streamlining the supply chain process.
Dealing with EDI Errors and Rejections
EDI 856 documents are prone to errors and rejections if they contain inaccuracies or fail to meet the required standards set by trading partners. To mitigate these issues, companies must implement thorough validation checks before transmission. If an error is detected, a functional acknowledgement, known as EDI 997, is sent to indicate that the transaction was received but cannot be processed further without corrections. Diligent monitoring of these acknowledgements allows businesses to address mistakes swiftly.
Common Errors:
- Incorrect or missing data segments
- Invalid product identifiers or quantities
- Inconsistencies with purchase order information
Solutions:
- Employ automated validation tools that check data accuracy in real-time
- Set up alerts for immediate notification upon receiving an EDI 997
- Establish standard operating procedures for resolving errors promptly
Addressing Issues with Trading Partners
Interactions with trading partners sometimes raise challenges, particularly when there are discrepancies in transaction standards or communication protocols. Each partner may have unique requirements for their EDI 856 transactions, making standardized communication arduous. To navigate these complexities, organizations should engage in proactive discussions with their trading partners to clarify expectations and develop a mutually beneficial EDI framework.
Frequent Issues:
- Divergent EDI standards and specifications
- Misalignment on shipment and receipt timelines
Solutions:
- Regularly review and update EDI guidelines in partnership agreements
- Standardize EDI setups as much as possible to facilitate smoother transactions
- Implement robust testing scenarios with new trading partners to prevent future disputes
Advanced Topics in EDI 856
As organizations strive for greater efficiency, the customization of EDI 856 to meet specific industry needs becomes crucial. Advanced topics focus on tailoring transaction sets for specialized applications and delving into the diverse demands of retail and the automotive sector.
Customization and Extending the Standard
Customization of the EDI 856 transaction set, also known as the Advance Shipping Notice (ASN), allows businesses to communicate shipment details in a manner that aligns with their unique operational procedures. This customization often involves extending the standard X12 transaction set to include additional data elements that are critical for a company’s internal processes and for ensuring compliance with their trading partners’ requirements.
- Sector-Specific Fields: Custom fields are added to address sector-specific needs, such as batch numbers in pharmaceuticals or production lot sizes in manufacturing.
- Enhanced Shipment Tracking: By customizing messages, companies can include granular shipment tracking details, thereby enhancing visibility and control over the supply chain.
Sector-Specific Use Cases: Retail and Automotive
In the retail and automotive industries, EDI 856 must cater to distinct needs that reflect the complexities of their supply chains. The document is optimized to handle the high volume of goods and the precision required in tracking shipments.
- Retail: Retailers often require a highly detailed ASN to streamline their inventory management, necessitating additional information such as item-level RFID tags or specific packaging hierarchies.
- Automotive: The automotive sector, on the other hand, might need extensive details on parts, sub-components, and their assembly into final products to maintain just-in-time (JIT) manufacturing processes.
- Retail: Retailers often require a highly detailed ASN to streamline their inventory management, necessitating additional information such as item-level RFID tags or specific packaging hierarchies.
Through sector-specific customization of EDI 856, companies in both retail and automotive industries can achieve more accurate and timely information exchange, which is essential for maintaining the integrity of their respective supply chains.
Leveraging EDI 856 for Inventory Management
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) 856, also known as the Advance Shipping Notice (ASN), is pivotal for enhancing inventory management operations. It facilitates immediate updates and precise tracking of goods across the supply chain.
Improving Inventory Visibility
As shipments are en route, inventory managers receive details about the contents of shipments, including item descriptions and quantities. This data ensures that retailers are equipped to:
- Track incoming shipments
- Prepare for storage and sales space requirements
- Update inventory records accurately and promptly
Receiving EDI 856 translates to knowing exactly which items will be replenished, allowing businesses to maintain optimal stock levels without overstocking or stockouts.
Integrating Shipment Data with Inventory Systems
An efficient inventory management system hinges on the integration of shipment data. EDI 856 provides a structured format for shipment information, allowing it to be seamlessly absorbed by an organization’s inventory systems. Critical elements include:
- Item descriptions: Specific details about the goods being shipped
- Quantities: Exact numbers of items within the shipment
- Purchase order number: Links the shipment to the original order
This structured data can be automatically fed into inventory management systems, minimizing manual entry errors and enhancing the overall efficiency of the supply chain. Robust integration results in accurate forecasting, improved order fulfillment rates, and optimizes the reconciliation process between received goods and purchase orders.
The Future of EDI 856 and Supply Chain Integration
EDI 856, commonly known as the Advance Shipping Notice (ASN), is a critical document in the logistics and supply chain sectors. Its role is expected to expand as it continues syncing business processes with the increasing pace of ecommerce and technological advancements.
Emerging Trends in Electronic Data Interchange
New technologies are shaping the future of Electronic Data Interchange (EDI), enhancing the capabilities of EDI 856. Trends include the integration of EDI with blockchain for improved transparency and the use of Artificial Intelligence to predict disruptions in the supply chain. These advancements facilitate real-time data exchanges, leading to precise tracking and inventory management.
- Blockchain: Ensures immutable records of transactions.
- Artificial Intelligence: Predictive analytics for efficient supply chain management.
The Role of EDI in Ecommerce and Fulfillment
In ecommerce, EDI 856 is pivotal for the fulfillment process. It communicates detailed shipment information to retailers and customers, enabling a seamless order-to-delivery cycle. As online shopping prevails, EDI 856 adapts to support new fulfillment strategies such as drop shipping and real-time stock updates.
- Drop shipping: Streamlines supply chain by shipping directly to the customer.
- Real-time stock updates: Keeps inventory data accurate and reduces overstock or stockouts.
Through these practices, EDI 856 remains essential in reducing errors, expediting shipping, and ensuring customer satisfaction in the dynamic world of ecommerce.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the EDI 856 transaction set, providing clarity on specifications, structure, and differences from related EDI documents.
How does the EDI 856 ASN differ from the EDI 810 Invoice?
Overall, the main difference between the EDI 856 ASN and the EDI 810 Invoice is their purpose and the type of information they convey. The ASN focuses on notifying the buyer about an upcoming shipment, while the Invoice focuses on requesting payment for goods or services already provided. Both documents play a crucial role in efficient supply chain management and financial transactions between trading partners.
What distinguishes an EDI 855 Purchase Order Acknowledgment from an EDI 856 ASN?
EDI 855 Purchase Order Acknowledgment is a document sent by the supplier to confirm the receipt of a purchase order from the buyer. It serves as a commitment from the supplier that the order will be fulfilled according to the terms and conditions outlined in the purchase order. The 855 acknowledgment acknowledges the receipt of the purchase order and indicates whether the supplier can fulfill the order as requested or if there are any discrepancies that need to be addressed.
EDI 856 Advanced Shipping Notice (ASN), on the other hand, is a document sent by the supplier to notify the buyer about the shipment of the goods. It includes detailed information about the contents of the shipment, such as item descriptions, quantities, packaging details, and shipping information. The 856 ASN helps the buyer anticipate the arrival of the goods and prepare to receive and process them efficiently.
Overall, the EDI 855 focuses on confirming the receipt and acceptance of a purchase order, while the EDI 856 ASN focuses on providing detailed information about the shipment of goods to facilitate efficient delivery and receipt processes.
Can you explain the typical implementation process for EDI 856?
The first step is to establish a connection between the sender’s and receiver’s systems to enable the exchange of electronic documents. This involves setting up a secure communication protocol, such as AS2 or FTP, to transmit the EDI 856 messages.
Next, the sender must generate and transmit the ASN to the receiver once the shipment has been prepared and is ready to be sent out. The ASN includes detailed information about the contents of the shipment, such as item descriptions, quantities, packaging details, and shipment identifiers. This information allows the receiver to track the shipment, reconcile it with their purchase order, and prepare for its arrival.
After the ASN has been transmitted, the receiver will process the information and update their systems accordingly. This may involve validating the data, confirming receipt of the shipment, and updating inventory levels. By integrating the ASN into their receiving process, organizations can streamline operations, reduce errors, and improve supply chain visibility.

